10 Common Retinal Disorders
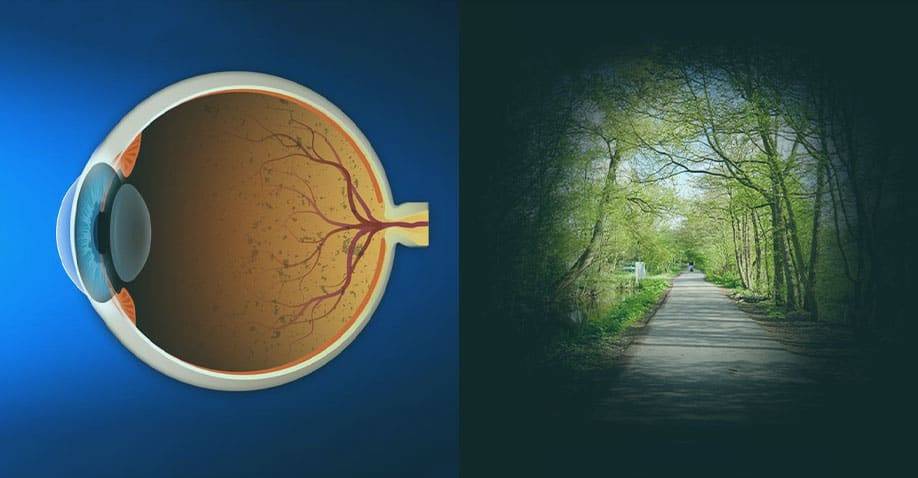
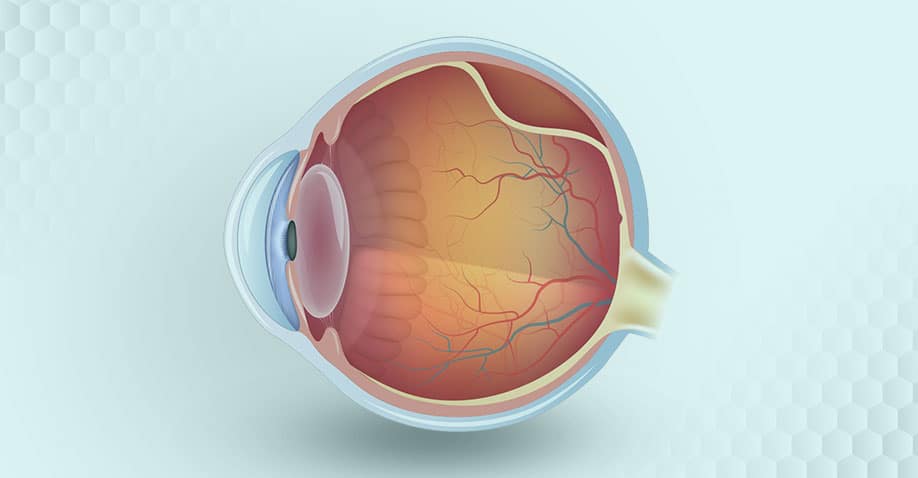
The eye, similar to a camera, has a lens in front which captures light entering the eye. The light is then focussed onto the thin layer of light-sensitive nerve tissue (similar to a camera film) that lines the back of the eye. The retina contains many light-sensitive photoreceptor cells which convert the light into electrochemical signals that are relayed to the vision center in the brain via the optic nerve. This information is processed by the brain and translated into the images we see. A healthy and intact retina is therefore crucial for good quality and clear vision.
Damage to any part of the retina or optic nerve can affect the way visual information is processed, leading to distorted or absent vision. There are various conditions and diseases that can affect the retina which typically results in visual problems or severe vision loss. This includes:
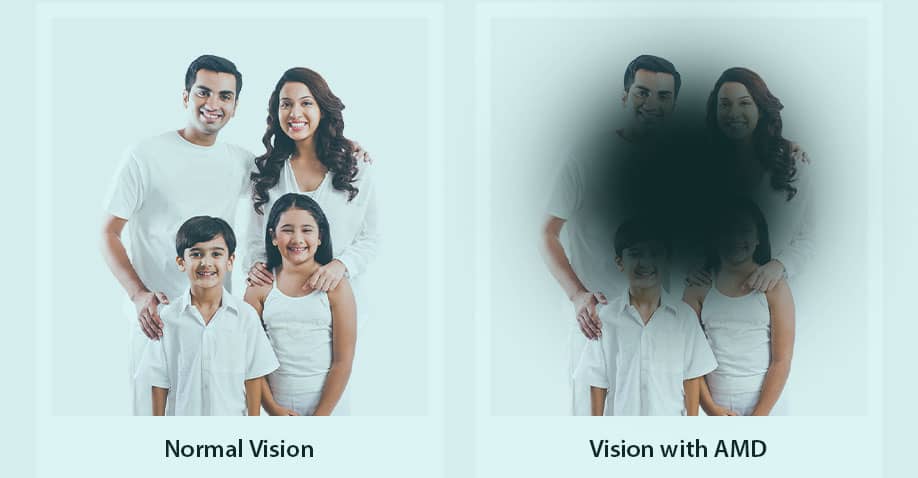
- Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) – a disorder where the center of the retina which is essential for detailed tasks requiring fine vision begins to deteriorate in people over the age of 60. Symptoms include blurred central vision or a blind spot in the center of the visual field.
- Diabetic Eye Disease – Over time, diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels and tissue of the retina. This can lead to conditions such as diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema which can cause vision complications.
- Retinal Tears – a crack or break in the thin layer of tissue lining the back of the eye (retina). This condition is often accompanied by sudden symptoms of floaters (specks in the field of vision) and flashing lights.
- Retinal Detachment – a condition where the retina pulls away from the underlying tissue layers that provide it nourishment (choroid layer). A retinal detachment is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment as the retina cannot reattach by itself and stops functioning, causing loss of vision.
- Macular Edema – The macula is surrounded by many tiny blood vessels (capillaries). Any condition that affects blood circulation in the eye or damages blood vessels in the retina can cause blood or fluid to accumulate or build up under the macula. This can cause the macula to swell and thicken which affects the proper functioning of the macula. Macular edema is often painless. Symptoms include blurred or wavy central vision, blind spots, faded colour vision, and sensitivity to bright lights.
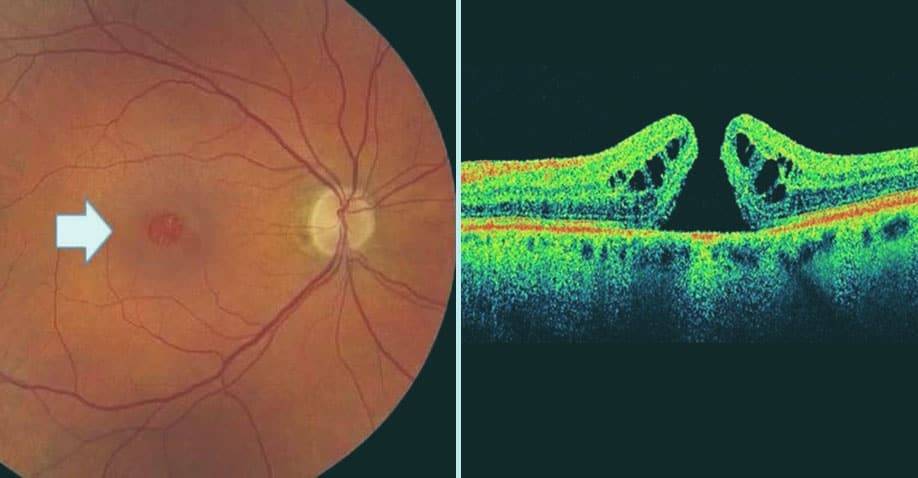
- Macular Hole – a small defect/break in the center of the retina (macula) which may develop in people over 60 due to an injury to the eye or from abnormal traction between the retina and the vitreous.
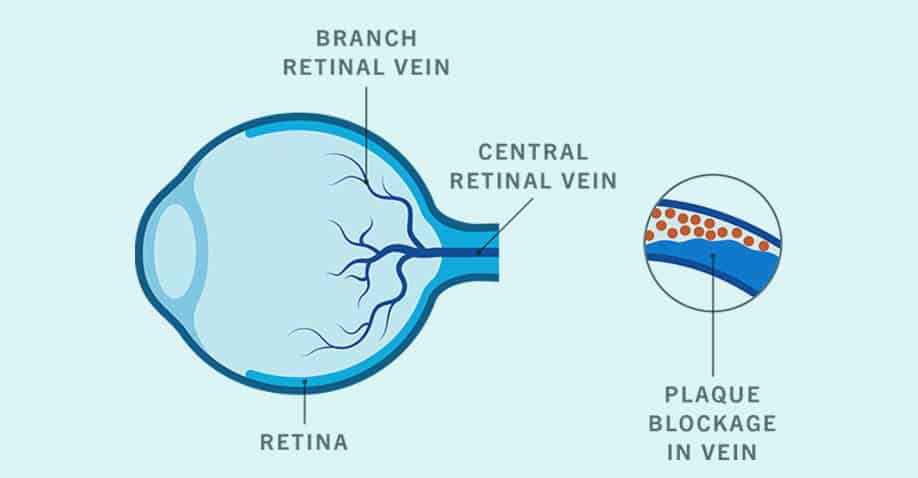
- Retinal Vascular Occlusion – a blockage in the small vessels (arteries and veins) that carry blood to or from the retina can cause blood or other fluids to build up and spill out onto the retina, leading to swelling. When this happens, the retina cannot interpret and transmit visual images properly. Without proper blood circulation, the nerve cells in the eye can die, leading to further vision loss.
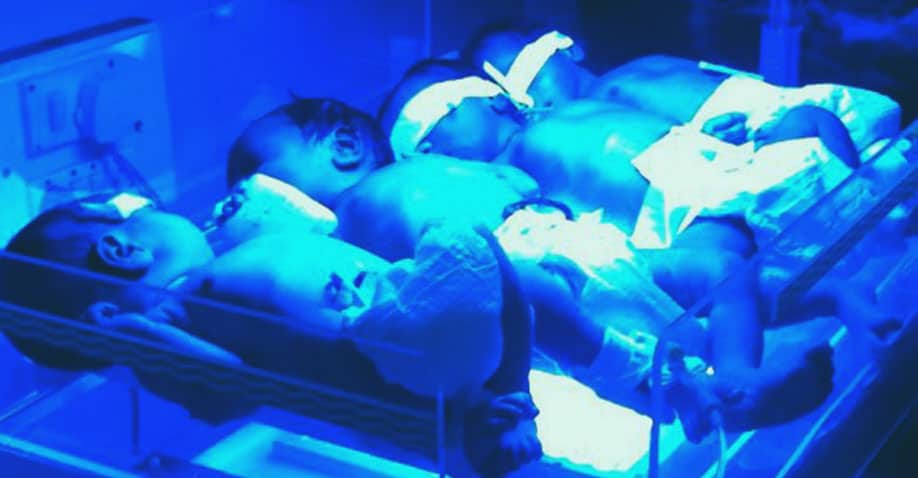
- Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP) – a disorder of the developing retinal blood vessels in babies that are born too soon or those with low birth weight. Premature birth can disrupt normal retinal blood vessel growth and cause abnormal vessels to develop randomly on the baby’s retina. These new blood vessels are fragile and can leak blood into the eye and cause scarring of the retina. If ROP is not detected in time and treated, the condition can worsen and result in serious vision impairment.
- Retinitis Pigmentosa – a hereditary and progressive retinal disease that affects approximately 1 in 4,000 people worldwide. In this condition, the photoreceptor cells which capture and process light in the retina to help us see degenerate and stop functioning over time. This leads to loss of or diminished night vision and peripheral vision.
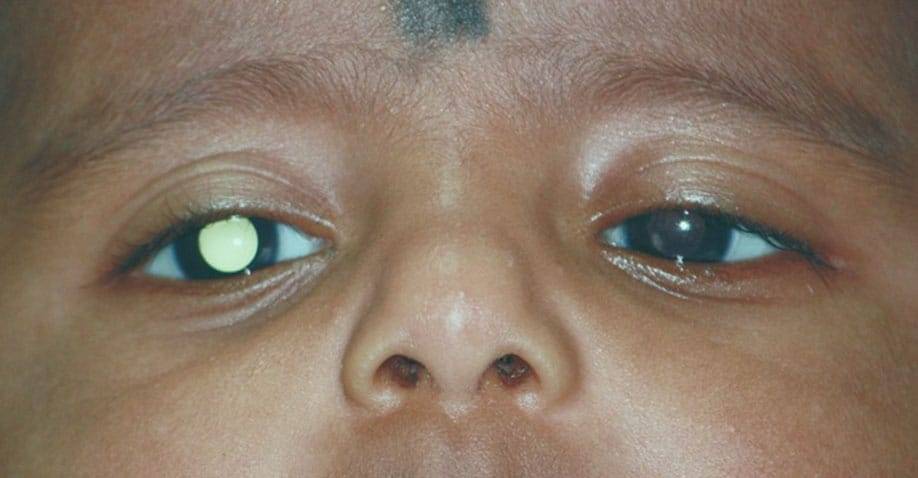
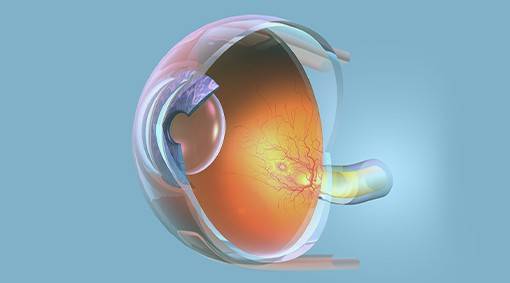
- Retinoblastoma – a life-threatening eye cancer that develops in the cells of the retina. This cancer, which is commonly seen in babies and young children, can affect vision and even lead to total blindness or loss of the entire eye if left untreated. It can also become a threat to life if it spreads outside the eye to the brain and other parts of the body.
If you notice any changes in your vision, it is essential to have your eyes examined by an eye doctor at the earliest to prevent vision complications. While some retinal disorders are mild and only affect a person’s vision temporarily, others are quite serious and can lead to permanent vision loss or blindness. Early detection and treatment may be able to prevent and delay the progression of most retinal disorders. Nearly all retinal disorders or diseases affecting the retina can be managed satisfactorily under the guidance of a trained retina specialist.
Read More Eye Care Blogs
4 Eye Problems That Can Result from Diabetes
If you are a diabetic, it means that the blood glucose or blood sugar in your body is too high. Most of the food you eat is broken down by your body into glucose - the main source of energy that is used for the various functions of the body. Insulin (a hormone made by...
Eye Safety at Home – Tips to Prevent Eye Injuries
ur homes are meant to be safe havens, but they can also be unexpected sources of danger, especially when it comes to eye injuries. Whether it's a mundane task like cooking, working in the yard or garden, Do-it-yourself projects, or even playtime...
Safeguarding Young Eyes – A Comprehensive Guide to Preventing Eye Injuries in Children
s parents, guardians, and caregivers, safeguarding our children's well-being is always at the forefront of our minds. Yet, amidst all the protective measures we take, we may inadvertently overlook a crucial aspect of their health - their eyes. Eye...