4 Eye Problems That Can Result from Diabetes
If you are a diabetic, it means that the blood glucose or blood sugar in your body is too high. Most of the food you eat is broken down by your body into glucose – the main source of energy that is used for the various functions of the body. Insulin (a hormone made by the pancreas) helps move the glucose from your blood into the cells to be used or stored for energy. With diabetes, your body either doesn’t create enough insulin or can’t use the insulin it makes efficiently. As a result, the glucose doesn’t reach your cells and starts to accumulate in your bloodstream. Elevated blood glucose levels in your blood can lead to swelling and inflammation throughout the body causing various health problems and damage to your eyes, nerves, kidneys, and other organs over time.
If you have diabetes, here is how high blood sugar can affect your eyes and vision:
1. Blurry Vision
High glucose levels in the blood can cause the tissues of your eyes to swell and affect the shape of your lens. This can make it hard for your eyes to focus properly and temporarily lead to blurred vision which goes away after your blood sugar stabilizes. Some people may also experience blurry vision for a few days or weeks when they start insulin treatment or change their diabetes medication.
2. Cataracts
Cataract is a clouding of the eye’s natural crystalline lens that blocks or alters the way light enters the eye. With age, the proteins in the eye form clumps and the lens gradually becomes more and more opaque and interferes with vision. Cataract can make things look blurry, hazy, or less colourful. The only treatment that’s currently available for cataract is a simple surgery to remove the cloudy lens and replace it with a clear, artificial one. While everyone will eventually develop cataracts, people with diabetes are more likely to develop cataracts earlier and the condition also progresses much faster in them.
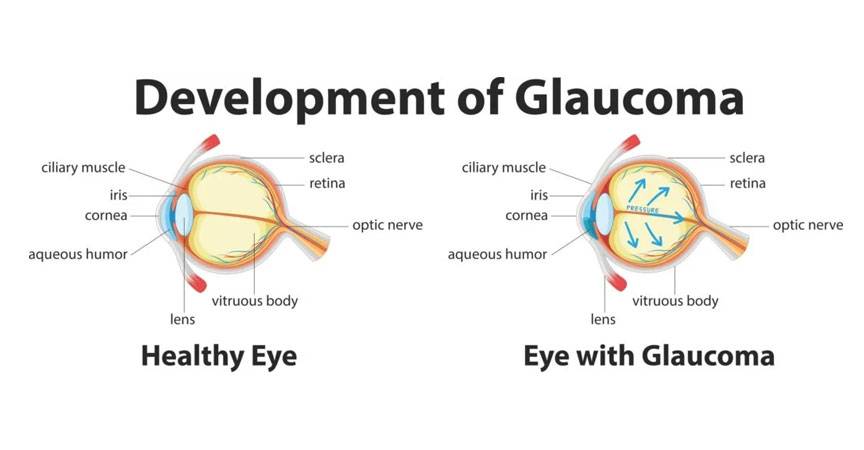
3. Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a serious eye condition caused by increased fluid pressure within the eye, which can damage the optic nerve that transmits images to the brain. Glaucoma is often nicknamed the ‘silent thief of sight’ as there are no early symptoms and before you notice anything unusual with your sight, significant vision loss may have already occurred.
In people with diabetes, high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina and result in the creation of abnormal new ones. These new blood vessels can block the eye’s natural drainage system and cause an increase in eye pressure and glaucoma. Studies indicate that people with diabetes have double the risk of developing glaucoma when compared to those that don’t.
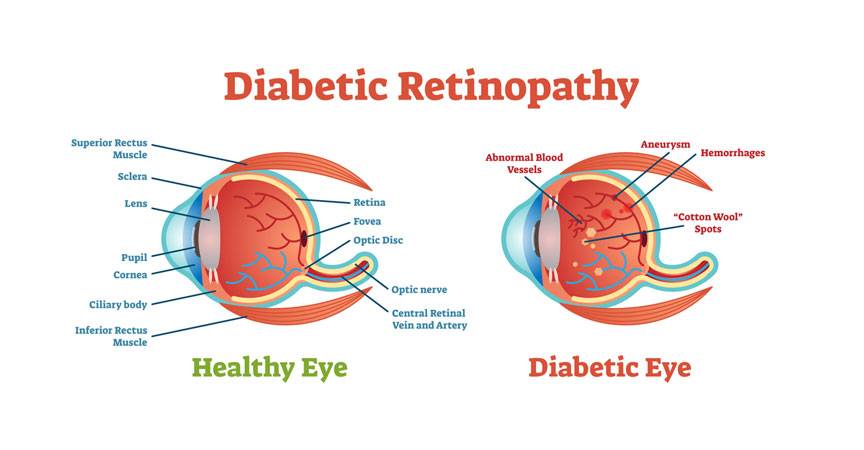
4. Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a type of progressive eye disease that affects people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sugar or glucose imbalances in the blood over a period of years can lead to the blockage of the tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina, cutting off its blood supply. This results in the growth of abnormal blood vessels on the retinal surface. Diabetic retinopathy occurs when these new blood vessels leak blood and other fluids, causing the retinal tissue to swell or form scar tissue, resulting in floaters and cloudy or blurred vision. Other serious retinal conditions such as Macular Edema, Macular Degeneration, and Retinal Detachment that can lead to permanent vision loss can arise from further complications of diabetic retinopathy.
Conclusion
- Diabetes can have a direct effect on the health of your eyes.
- Those with uncontrolled or chronic high blood sugar levels are at a higher risk for eye disease.
- If you have diabetes, consult a diabetes specialist who can recommend a proper diet and medication to ensure that your eyes and the rest of your body stay healthy as you age.
- If you have a diagnosis of diabetes-related eye problems, the best thing you can do is to watch your sugar intake and take preventative measures to regulate blood sugar levels to preserve vision and ensure it doesn’t worsen in the years to come.
- This includes following an eye-healthy diet to help reduce inflammation and exercising regularly to maintain healthy body weight and improve your overall health. A dilated eye exam once a year can help your eye doctor check for any vision complications and find problems early when they’re easier to treat and prevent permanent vision loss. While mild problems may be treated by controlling your blood sugar levels, advanced cases may require laser treatment or surgery.
Read More Eye Care Blogs
Eye Safety at Home – Tips to Prevent Eye Injuries
ur homes are meant to be safe havens, but they can also be unexpected sources of danger, especially when it comes to eye injuries. Whether it's a mundane task like cooking, working in the yard or garden, Do-it-yourself projects, or even playtime...
Safeguarding Young Eyes – A Comprehensive Guide to Preventing Eye Injuries in Children
s parents, guardians, and caregivers, safeguarding our children's well-being is always at the forefront of our minds. Yet, amidst all the protective measures we take, we may inadvertently overlook a crucial aspect of their health - their eyes. Eye...
Celebrate Deepawali Safely – Eye Safety Tips for a Bright and Injury-Free Festival
Celebrate Deepawali Safely - Eye Safety Tips for a Bright and Injury-Free Festival eepawali, the festival of lights, is a time of celebration and joy for millions of people in India and across the world. It's a time when families come together,...